

Next: Conclusions
Up: Mathematical Description of the
Previous: Perfect Gas Hodograph Equation
Of course, the hodograph method would be useless if we could not
transform the solution back to the physical plane. For completeness,
the reverse transformation is given.
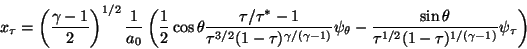 |
(22) |
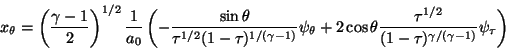 |
(23) |
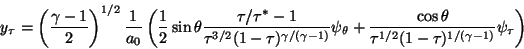 |
(24) |
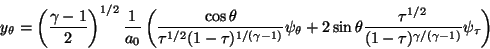 |
(25) |
After Equation 14 or 21 is employed
to find 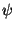 ,
Equations 22-25 are
integrated to find the x and y coordinates of the streamline.
,
Equations 22-25 are
integrated to find the x and y coordinates of the streamline.
Carl Banks
1999-05-14